comprehensive guide to Cloud Computing for Big Data: Transforming Analytics at Scale 2024
In today’s interconnected world, organizations are generating unprecedented amounts of data from web applications, social media, IoT devices, and enterprise systems. Managing and analyzing this Big Data is no small feat. Cloud computing has emerged as an ideal platform for handling the complexity and scale of Big Data, offering flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency.
This blog explores how cloud computing powers Big Data analytics, its key characteristics, deployment models, and service types.
What is Cloud Computing?
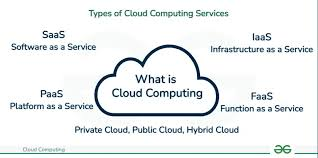
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services—such as servers, storage, databases, networking, and software—over the Internet (the cloud). It provides on-demand access to a shared pool of configurable resources, enabling organizations to scale up or down as needed.
Key Characteristics:
- On-Demand Self-Service:
- Users can provision computing resources automatically without human intervention.
- Broad Network Access:
- Resources are accessible from anywhere via the Internet.
- Resource Pooling:
- Resources are shared among multiple users dynamically.
- Rapid Elasticity:
- Scales quickly to meet demand.
- Measured Service:
- Pay-as-you-go pricing ensures cost efficiency.
Why Cloud Computing for Big Data?
Big Data analytics and cloud computing share fundamental principles:
- Distributed Computing:
- Both leverage clusters of devices for storage and processing.
- Scalability:
- Cloud platforms handle the exponential growth of data effortlessly.
Cloud computing offers:
- Massive Storage:
- Unlimited storage capabilities for structured and unstructured data.
- High Performance:
- Distributed processing ensures quick analysis of large datasets.
- Flexibility:
- Supports a wide variety of tools and frameworks like Hadoop, Spark, and MapReduce.
- Cost Efficiency:
- Pay-as-you-go models minimize infrastructure investment.
The 3-4-5 Rule of Cloud Computing
3 Service Models
- Software as a Service (SaaS):
- Access to cloud-based applications without managing the underlying infrastructure.
- Example: Social media analytics tools.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS):
- A platform for developing, deploying, and managing applications.
- Example: Platforms preloaded with Hadoop or Spark.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
- On-demand access to fundamental computing resources like storage, servers, and networking.
- Example: AWS EC2 or Google Compute Engine.
4 Deployment Models
- Public Cloud:
- Resources are shared among multiple organizations and managed by a third-party provider.
- Example: AWS, Azure.
- Private Cloud:
- Dedicated resources for a single organization, offering enhanced security.
- Example: On-premise cloud setups for sensitive data.
- Hybrid Cloud:
- Combines public and private clouds for flexibility and optimized workloads.
- Example: Data-sensitive operations in a private cloud, analytics in a public cloud.
- Community Cloud:
- Shared infrastructure for organizations with common goals, such as healthcare compliance.
5 Key Characteristics
- On-Demand:
- Resources are available anytime, anywhere.
- Networked Access:
- Broad accessibility ensures remote collaboration.
- Elasticity:
- Adapts dynamically to changing workloads.
- Measured Usage:
- Pay only for what you use.
- Resource Pooling:
- Shared resources for efficiency and cost savings.
Cloud Services for Big Data Analytics

- SaaS for Big Data:
- Prebuilt analytics tools for social media monitoring, customer feedback, and more.
- Example: Sentiment analysis tools provided as a service.
- PaaS for Big Data:
- Offers platforms with ready-to-use environments for Hadoop, Spark, and other big data frameworks.
- Example: Azure Synapse Analytics.
- IaaS for Big Data:
- Provides the computational power and storage needed for large-scale processing.
- Example: AWS S3 for storage and EC2 for computing.
Popular Cloud Providers for Big Data
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Services: S3, Redshift, DynamoDB, Elastic MapReduce (EMR).
- Applications: High-performance computing, scalable storage for analytics.
2. Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Services: BigQuery, Dataflow, Google Compute Engine.
- Applications: Real-time data analytics and predictive modeling.
3. Microsoft Azure
- Services: Azure Data Lake, HDInsight, Synapse Analytics.
- Applications: Enterprise-scale analytics and integration with Microsoft products.
Real-World Applications
1. Retail
- Use Case: Personalized marketing campaigns based on customer behavior.
- Solution: Cloud-based analytics platforms process transaction data in real-time.
2. Finance
- Use Case: Fraud detection in credit card transactions.
- Solution: Real-time analytics on cloud platforms detect anomalies instantly.
3. Healthcare
- Use Case: Analyzing patient data for disease prediction.
- Solution: PaaS platforms with AI capabilities enhance diagnostic accuracy.
4. Social Media
- Use Case: Sentiment analysis of trending topics.
- Solution: SaaS tools for text and emotion analysis.
Challenges of Cloud Computing for Big Data
- Data Security:
- Ensuring privacy and protection of sensitive data.
- Data Latency:
- Delays in accessing or processing data from remote cloud servers.
- Cost Management:
- Optimizing resource usage to avoid overspending.
- Integration:
- Seamless integration with existing on-premise systems.
Future Trends in Cloud Computing for Big Data
- Serverless Computing:
- Fully managed services eliminating infrastructure management.
- AI Integration:
- Cloud-native AI tools for enhanced analytics capabilities.
- Edge Computing:
- Processing data closer to its source for reduced latency.
- Sustainability:
- Green cloud initiatives to reduce energy consumption in data centers.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has transformed how organizations approach Big Data analytics, offering unmatched scalability, cost efficiency, and flexibility. Whether it’s storing terabytes of data, running complex analytics, or delivering real-time insights, cloud platforms empower businesses to turn data into a strategic asset.
Are you ready to leverage the power of cloud computing for your Big Data needs? Start your journey today and unlock new possibilities!