Understanding Modern Data Storage Infrastructure: Types, Architectures, and Best Practices 2024
Data storage is a cornerstone of modern data engineering, enabling efficient data ingestion, transformation, and serving. As data volumes grow exponentially, organizations rely on advanced storage architectures to ensure scalability, durability, and accessibility.
This guide explores: ✅ Key components of modern storage infrastructure
✅ File, Block, and Object Storage
✅ Cloud storage solutions
✅ Streaming storage and caching
✅ Best practices for data storage efficiency
1. The Role of Data Storage in Modern Infrastructure

Data storage systems store, manage, and retrieve data efficiently across distributed environments.
✅ Why Data Storage Matters?
- Ensures reliability and durability for large datasets.
- Enables real-time and batch data processing.
- Supports high-performance computing and analytics.
- Integrates with cloud computing, AI, and machine learning.
💡 Example: A banking system relies on real-time storage for transaction processing while keeping historical data in a data lake for compliance.
🚀 Challenge: Choosing the right storage solution depends on factors like latency, cost, and scalability.
2. Data Storage Layering
Data storage follows a layered architecture that aligns with different data processing stages.
| Storage Layer | Function |
|---|---|
| Raw Data Storage | Stores unprocessed, raw data (Data Lakes, Hadoop HDFS). |
| Processed Storage | Stores structured data after transformations (Data Warehouses, SQL Databases). |
| Analytics & Serving | Supports reporting, AI, and machine learning (Cloud Data Warehouses, In-Memory Storage). |
💡 Example:
- Amazon S3 for raw data storage.
- Snowflake for structured analytics-ready data.
- Redis for caching frequently accessed datasets.
🚀 Best Practice: Optimize storage costs by using a multi-tiered architecture (cold, warm, hot storage).
3. Types of Data Storage Systems
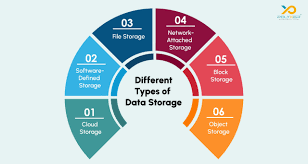
A. File Storage
File storage is a hierarchical storage system where data is stored in directories and files.
✅ Key Features:
- Organizes files into folders and subdirectories.
- Supports append operations and random access.
- Used in local disks, NAS (Network-Attached Storage), and Cloud File Systems.
🔹 Examples:
| Storage Type | Example Solutions |
|---|---|
| Local File Storage | NTFS (Windows), ext4 (Linux) |
| Network File Storage (NAS) | Amazon EFS, Azure File Storage |
| Cloud File Systems | Google Cloud Filestore, AWS FSx |
💡 Use Case: Media companies store large video and image files in NAS systems for quick retrieval.
🚀 Best Practice: Use distributed file systems (HDFS, EFS) for handling large-scale workloads.
B. Block Storage
Block storage divides data into fixed-size blocks and optimizes access speed.
✅ Key Features:
- Provides low-latency, high-performance access.
- Used in databases, virtual machines, and boot disks.
- Common in on-premises SAN (Storage Area Networks) and cloud block storage.
🔹 Examples:
| Storage Type | Example Solutions |
|---|---|
| Local Block Storage | RAID, NVMe SSDs |
| Cloud Block Storage | Amazon EBS, Azure Managed Disks |
💡 Use Case: E-commerce platforms use block storage for transactional databases to ensure fast query processing.
🚀 Best Practice: Use RAID configurations for fault tolerance and performance optimization.
C. Object Storage
Object storage is scalable and flexible, storing data as objects with metadata.
✅ Key Features:
- Stores unstructured data (images, videos, logs).
- Supports high scalability with low-cost cloud storage.
- Used in data lakes, backup storage, and serverless applications.
🔹 Examples:
| Storage Type | Example Solutions |
|---|---|
| On-Prem Object Storage | MinIO, Ceph |
| Cloud Object Storage | Amazon S3, Azure Blob Storage, Google Cloud Storage |
💡 Use Case: Big data platforms use object storage for log retention and AI model training datasets.
🚀 Best Practice: Store cold data in object storage for cost efficiency while keeping frequently accessed data in caching layers.
4. Distributed & Cloud Storage Solutions
🔹 Why Distributed Storage?
- Handles massive data volumes across multiple nodes.
- Ensures fault tolerance and redundancy.
- Used in Hadoop, Apache Spark, and cloud data warehouses.
✅ Popular Distributed Storage Solutions:
| Technology | Use Case |
|---|---|
| HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System) | Big Data processing |
| Amazon S3 | Cloud object storage |
| Google Cloud Storage | Scalable multi-region storage |
| Azure Data Lake Storage | Large-scale data analytics |
🚀 Best Practice: Use distributed object storage for high availability and cost optimization.
5. Streaming & Memory-Based Storage
A. Streaming Storage
🔹 Stores real-time event streams before processing.
✅ Key Features:
- Supports message retention and replay.
- Enables low-latency real-time analytics.
🔹 Popular Streaming Storage Solutions:
| Technology | Provider |
|---|---|
| Apache Kafka | Open Source |
| Amazon Kinesis | AWS |
| Google Pub/Sub | Google Cloud |
💡 Use Case: Stock market platforms use Kafka to store live trading data for analytics.
🚀 Best Practice: Set retention policies to balance storage cost vs. real-time processing needs.
B. Memory-Based Storage (Caching)
🔹 Why Caching?
- Reduces query latency by storing frequently accessed data in memory.
- Used in database query acceleration, web caching, and AI workloads.
✅ Popular Caching Technologies:
| Technology | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Redis | High-speed database caching |
| Memcached | API call caching |
| Amazon ElastiCache | Cloud-based caching |
💡 Use Case: E-commerce platforms cache product pages to reduce loading times.
🚀 Best Practice: Implement cache expiration policies to avoid stale data issues.
6. Best Practices for Data Storage Efficiency

✅ Choose the Right Storage Type:
- Use object storage for logs and backups.
- Use block storage for databases.
- Use file storage for user files and application logs.
✅ Optimize for Cost and Performance:
- Store cold data in low-cost storage (S3 Glacier, Google Archive Storage).
- Keep hot data in fast SSD storage.
✅ Enable Data Governance & Compliance:
- Ensure GDPR, HIPAA compliance for sensitive data.
- Implement access control and encryption for security.
🚀 Hybrid storage strategies (multi-cloud, tiered storage) provide cost and performance balance.
7. Final Thoughts
Modern data storage architectures power AI, analytics, and cloud-native applications. Choosing the right mix of file, block, object, and cloud storage enables efficiency, cost optimization, and scalability.
💡 What storage architecture does your organization use? Let’s discuss in the comments! 🚀